The essential component of every IV therapy is a sterile saline solution. The solution is either used alone to rehydrate the patient or in combination with other nutrients, medications, or supplements. Because the ingredients of the IV drip bag are administered directly to the bloodstream, body cells absorb them quickly and efficiently.
This article lists the main types of IV fluids, their chemical composition, and the medical conditions they help treat.

Note: Learn more about what is IV therapy and how it works.
IV fluids are broadly classified into two groups: crystalloid and colloid solutions. These are further divided into categories based on tonicity (crystalloid) and whether they contain natural or artificial ingredients (colloid).
Crystalloid solutions are divided into three subtypes:
Colloid solutions can be categorized into two subtypes:
Based on the unique characteristics of each fluid type, healthcare workers prescribe a suitable therapy for each patient.
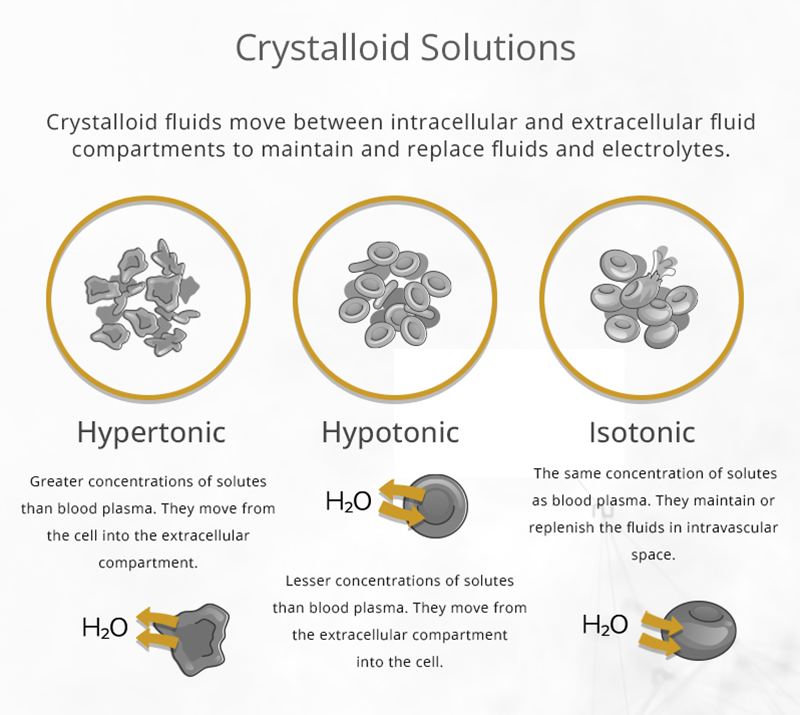
Crystalloid solutions contain smaller particles or solutes that easily pass through cell membranes. Crystalloid solutions are divided based on tonicity into hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic solutions.
Tonicity is the ability of a solution to make water move in or out of a cell. This ability depends on the concentration of solutes in relation to the surrounding blood plasma.
1. Hypertonic Solutions
Hypertonic solutions contain a greater concentration of solutes than the patient’s cells. Because of this, they cause the fluids to move out of the cell into the extracellular fluid compartment. As a result, the cells shrink.
Depending on the formulation, hypertonic fluids are used to help patients with post-operative recovery, severe sodium deficiency, swelling of the brain, severe bronchitis, low blood sugar, and more.
They should be used for short periods because they can cause fluid overload, which leads to the buildup of fluids in the lungs.
2. Hypotonic Solutions
Hypotonic solutions contain smaller concentrations of solutes than the patient’s cells, causing water to move from the extracellular fluid compartment into the cell. Nutritional IV providers use these fluids for patients with dehydrated cells, often caused by diabetic ketoacidosis, high blood glucose, a hangover, etc.
Note: Hypotonic solutions also aid recovery after strenuous exercise. Learn more about IV Therapy for Athletic Performance.
3. Isotonic Solutions
Isotonic crystalloid fluids have the same concentration of solutes as the patient’s cells. They are used to replenish fluid deficits in the extracellular fluid compartment or maintain its volume.
Depending on the formulation, they help treat patients suffering from blood loss after surgery, dehydration, and sodium loss caused by vomiting and diarrhea, hemorrhages, metabolic acidosis, etc.
Note: Learn more about isotonic IV fluids for rehydration, including who can receive them and when.

Colloid solutions have larger particles than crystalloid fluids. They typically don’t cross cell membranes but remain in the bloodstream, providing the patients with nutrients for longer periods than crystalloid solutions.
Colloid fluids increase intravascular volume and raise blood pressure in patients with blood and fluid losses that occur due to hypovolemic shock, capillary leak syndrome, cardiac disease, edema, and low oncotic pressure.
Colloids are divided into natural and synthetic fluids.
1. Natural Colloids
Natural colloid fluids contain proteins and blood products such as plasma and blood-clotting constituents. Colloid fluids commonly contain these ingredients:
2. Synthetic Colloids
Synthetic colloids are alternative, economical solutions to albumin fluids. Common synthetic colloid fluids include starches, dextrans, and gelatins.
There are several types of IV fluids, and not all of them are strictly for medicinal use. Nutritional IV therapy is a great way of replenishing your body with vitamins and minerals.
Whatever the case may be, your IV therapy provider will determine the best type of IV fluid based on your medical history, current condition, and needs.
If you are looking for nutritional IV therapy in the Phoenix area, Vibrant Vitality Clinic is the place to go to. Our team of professionals will determine the optimal mix of nutrients for you based on your needs. Contact us for more information or to book an appointment.




4325 E Indian School Rd, Suite 130
Phoenix, AZ 85018
United States
(480) 422-2058
info@vibrantvitalityclinic.com
Monday - Friday: 9:00 am - 6:00 pm
Saturday: 9:00 am - 3:00 pm
Sunday: Closed
